

HOOF
Properties of Wool
-
warm
-
Hygroscopic
-
Acoustic Absoption
-
Fire resistant
-
Natural and Renewable
-
Sunsafe
-
Biodegradabe
-
Breathable
-
Non-allergenic
-
Durable and Elastic
-
Naturally Insulating
-
Easy to care


Uses of Wool


•Very fine, white Merino can be dyed and is uesed for making soft fabrics.
•Soft and off-colored wool from a drysdale makes a fabric too coarse.
•Strong and coarse wool is used to make carpets and curtains.
•Short and discolored wool is used for insulation, or for absorbing industrial spills.
•protein from wool can be used in cosmestic and medicine industry.(Alistair Nicol, 2012)
Wool grading and the uses are determined by considering certain qualities like fineness, length, color and appearance.
1) American blood system: It is used to compare one flock with another.
2) The English or spinning count system: It uses a measurement called “spinning count” and provides us with narrow ranges and a precise nomenclature than American system.
3) Micron system: In this system individual fibers are accurately measured. Microscopes and a background slide with micron crosshairs are used for comparison. It is measured in microns and its fineness is expressed as the mean fiber diameter.

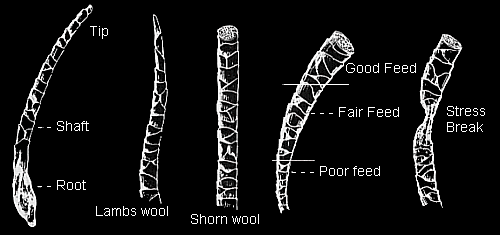
wool grading

1 micron= 1/1000000th m or 1/25000th inch
The wool is graded in micron. The higher the number of micron, the lower the quality and the price.


Wool Structure

1.Wools approximate elementary composition:
Hydrogen-7%, Nitrogen-17%, Oxygen-20%, sulphur-6%.
2.Wool has unique and exceptional properties which the other fibers do not have. it is able to provide us with coolness in summer and warmth in winter. It has biological composite structures like cuticle and cortex.
3.The chemical composition of wool consist of 80% keratin and 19% non-keratin proteins;1% internal lipids. Wool's chemical structure is formed by Cystine bonds, hydrogen bonds, salt linkages and also have hydrophobic interactins. It decomposes at 250 C and its isotonic point is when pH is at 4.9. (Rouette, 2012).
4.The wool gathered by the farmers is classified before it is sold, this means that the wool is examined in its raw state. Factors like environmental, management and genetic factors have an influence on the wool's properties including fibre diameter, length, tensile and yield.
REFERENCE:
Wool Properties. (2015). Retrieved from The woolly shepherd : http://www.woollyshepherd.co.uk/wool-properties/
The Wonders Of Wool. (2015). Retrieved from The campaign for wool. http://www.campaignforwool.co.nz/wool/
Alistair Nicol, C. S. (2012, July 13). Te Ara. Retrieved from Meat and wool - Wool production and processing: http://www.teara.govt.nz/en/meat-and-wool/page-6
Rouette, e. (2012, dec 15). khondoker. Retrieved from khondoker organization: http://khondoker.org/cgi-bin/weblog_basic/index.php?p=128
D.E.A Yarns. (n.d). Retrieved from Deayarns : http://www.deayarns.co.nz/woolquality.htm
Kott, R. (1993, july). Montguide wool grading . Retrieved from msuextension:http://store.msuextension.org/publications/AgandNaturalResources/MT198380AG.pdf
Wool Grading by the American Blood Count System. (n.d). Retrieved from Gfwsheep:http://gfwsheep.com/blood.count.html